5장 JobRepository와 메타데이터
- Job Repository
- 상태관리 : 잡의 상태를 Repository에 저장
- 배치 잡 실행 중 오류 발생 시 복구
- 실행 중 오류 발생 시 처리 유무
- 잡이 다시 실행되면 상태 트랙킹
- 잡의 재시작 및 아이템 재처리 시 동작 수행 결정
- 모니터링
- 실행 중 값 파악
- 잡 처리 시간/ 오류로 재시작 된 아이템 수 등
- 잡의 실행 진행 파악
- 실행 중 값 파악
- 상태관리 : 잡의 상태를 Repository에 저장
JobRepository 란?
- JobRepository Interface
Source
public interface JobRepository {
/**
* Check if an instance of this job already exists with the parameters
* provided.
*
* @param jobName the name of the job
* @param jobParameters the parameters to match
* @return true if a {@link JobInstance} already exists for this job name
* and job parameters
*/
boolean isJobInstanceExists(String jobName, JobParameters jobParameters);
/**
* Create a new {@link JobInstance} with the name and job parameters provided.
*
* @param jobName logical name of the job
* @param jobParameters parameters used to execute the job
* @return the new {@link JobInstance}
*/
JobInstance createJobInstance(String jobName, JobParameters jobParameters);
/**
* Create a new {@link JobExecution} based upon the {@link JobInstance} it's associated
* with, the {@link JobParameters} used to execute it with and the location of the configuration
* file that defines the job.
*
* @param jobInstance {@link JobInstance} instance to initialize the new JobExecution.
* @param jobParameters {@link JobParameters} instance to initialize the new JobExecution.
* @param jobConfigurationLocation {@link String} instance to initialize the new JobExecution.
* @return the new {@link JobExecution}.
*/
JobExecution createJobExecution(JobInstance jobInstance, JobParameters jobParameters, String jobConfigurationLocation);
/**
* <p>
* Create a {@link JobExecution} for a given {@link Job} and
* {@link JobParameters}. If matching {@link JobInstance} already exists,
* the job must be restartable and it's last JobExecution must *not* be
* completed. If matching {@link JobInstance} does not exist yet it will be
* created.
* </p>
*
* <p>
* If this method is run in a transaction (as it normally would be) with
* isolation level at {@link Isolation#REPEATABLE_READ} or better, then this
* method should block if another transaction is already executing it (for
* the same {@link JobParameters} and job name). The first transaction to
* complete in this scenario obtains a valid {@link JobExecution}, and
* others throw {@link JobExecutionAlreadyRunningException} (or timeout).
* There are no such guarantees if the {@link JobInstanceDao} and
* {@link JobExecutionDao} do not respect the transaction isolation levels
* (e.g. if using a non-relational data-store, or if the platform does not
* support the higher isolation levels).
* </p>
*
* @param jobName the name of the job that is to be executed
*
* @param jobParameters the runtime parameters for the job
*
* @return a valid {@link JobExecution} for the arguments provided
*
* @throws JobExecutionAlreadyRunningException if there is a
* {@link JobExecution} already running for the job instance with the
* provided job and parameters.
* @throws JobRestartException if one or more existing {@link JobInstance}s
* is found with the same parameters and {@link Job#isRestartable()} is
* false.
* @throws JobInstanceAlreadyCompleteException if a {@link JobInstance} is
* found and was already completed successfully.
*
*/
JobExecution createJobExecution(String jobName, JobParameters jobParameters)
throws JobExecutionAlreadyRunningException, JobRestartException, JobInstanceAlreadyCompleteException;
/**
* Update the {@link JobExecution} (but not its {@link ExecutionContext}).
*
* Preconditions: {@link JobExecution} must contain a valid
* {@link JobInstance} and be saved (have an id assigned).
*
* @param jobExecution {@link JobExecution} instance to be updated in the repo.
*/
void update(JobExecution jobExecution);
/**
* Save the {@link StepExecution} and its {@link ExecutionContext}. ID will
* be assigned - it is not permitted that an ID be assigned before calling
* this method. Instead, it should be left blank, to be assigned by a
* {@link JobRepository}.
*
* Preconditions: {@link StepExecution} must have a valid {@link Step}.
*
* @param stepExecution {@link StepExecution} instance to be added to the repo.
*/
void add(StepExecution stepExecution);
/**
* Save a collection of {@link StepExecution}s and each {@link ExecutionContext}. The
* StepExecution ID will be assigned - it is not permitted that an ID be assigned before calling
* this method. Instead, it should be left blank, to be assigned by {@link JobRepository}.
*
* Preconditions: {@link StepExecution} must have a valid {@link Step}.
*
* @param stepExecutions collection of {@link StepExecution} instances to be added to the repo.
*/
void addAll(Collection<StepExecution> stepExecutions);
/**
* Update the {@link StepExecution} (but not its {@link ExecutionContext}).
*
* Preconditions: {@link StepExecution} must be saved (have an id assigned).
*
* @param stepExecution {@link StepExecution} instance to be updated in the repo.
*/
void update(StepExecution stepExecution);
/**
* Persist the updated {@link ExecutionContext}s of the given
* {@link StepExecution}.
*
* @param stepExecution {@link StepExecution} instance to be used to update the context.
*/
void updateExecutionContext(StepExecution stepExecution);
/**
* Persist the updated {@link ExecutionContext} of the given
* {@link JobExecution}.
* @param jobExecution {@link JobExecution} instance to be used to update the context.
*/
void updateExecutionContext(JobExecution jobExecution);
/**
* @param jobInstance {@link JobInstance} instance containing the step executions.
* @param stepName the name of the step execution that might have run.
* @return the last execution of step for the given job instance.
*/
@Nullable
StepExecution getLastStepExecution(JobInstance jobInstance, String stepName);
/**
* @param jobInstance {@link JobInstance} instance containing the step executions.
* @param stepName the name of the step execution that might have run.
* @return the execution count of the step within the given job instance.
*/
int getStepExecutionCount(JobInstance jobInstance, String stepName);
/**
* @param jobName the name of the job that might have run
* @param jobParameters parameters identifying the {@link JobInstance}
* @return the last execution of job if exists, null otherwise
*/
@Nullable
JobExecution getLastJobExecution(String jobName, JobParameters jobParameters);
}
데이터 저장소
스프링 배치가 제공하며 RDB나 인메모리형식으로 제공한다.
스키마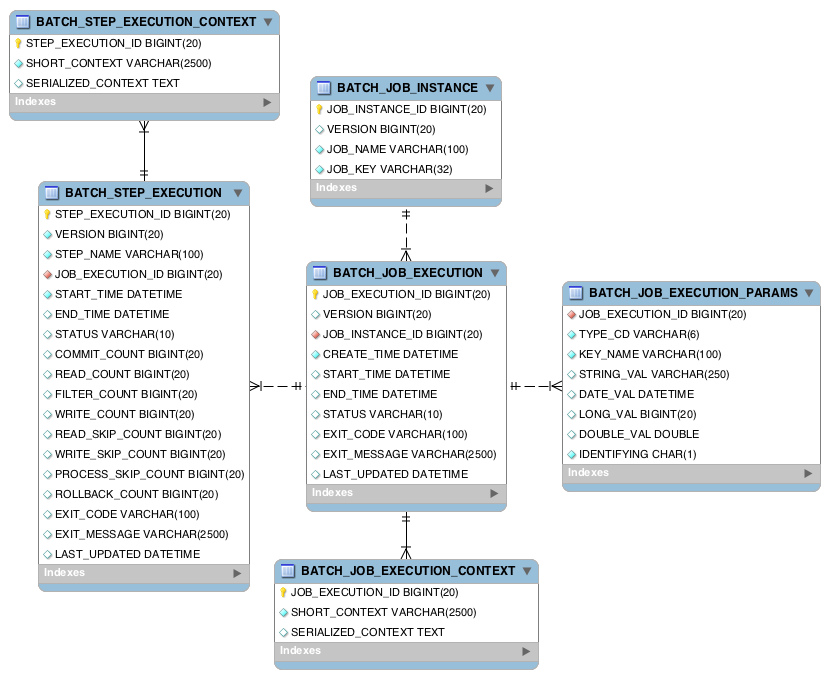
[BATCH_JOB_INSTANCE 테이블]
JobInstance에 관한 정보 저장.
| 필드 | 설명 |
|---|---|
| JOB_EXECUTION_ID | 기본키 |
| VERSION | 낙관적인 Lock에 사용. 레코드가 업데이트 될 때마가 버전 증가. 동일한 Job Repository를 사용하는 배치가 다른 시스템에서 동시에 같은 레코드에 접근할 때 이를 막기 위해 사용. 해당 문제 발생 시 OptimisticLockingFailureException 발생 |
| JOB_NAME | 잡 이름 |
| JOB_KEY | Job 이름과 파라메터의 해시값. Job Instance를 고유하게 식별하기 위해 사용 |
JdbcStepExecutionDao class - updateStepExecution()
@Override
public void updateStepExecution(StepExecution stepExecution){
validateStepExecution(stepExecution);
Assert.notNull(stepExecution.getId(),"StepExecution Id cannot be null. StepExecution must saved"
+" before it can be updated.");
// Do not check for existence of step execution considering
// it is saved at every commit point.
String exitDescription=truncateExitDescription(stepExecution.getExitStatus().getExitDescription());
// Attempt to prevent concurrent modification errors by blocking here if
// someone is already trying to do it.
synchronized (stepExecution){
Integer version=stepExecution.getVersion()+1;
Object[]parameters=new Object[]{stepExecution.getStartTime(),stepExecution.getEndTime(),
stepExecution.getStatus().toString(),stepExecution.getCommitCount(),stepExecution.getReadCount(),
stepExecution.getFilterCount(),stepExecution.getWriteCount(),
stepExecution.getExitStatus().getExitCode(),exitDescription,version,
stepExecution.getReadSkipCount(),stepExecution.getProcessSkipCount(),
stepExecution.getWriteSkipCount(),stepExecution.getRollbackCount(),
stepExecution.getLastUpdated(),stepExecution.getId(),stepExecution.getVersion()};
int count=getJdbcTemplate()
.update(getQuery(UPDATE_STEP_EXECUTION), parameters,
new int[]{Types.TIMESTAMP,Types.TIMESTAMP,Types.VARCHAR,Types.INTEGER,Types.INTEGER,
Types.INTEGER,Types.INTEGER,Types.VARCHAR,Types.VARCHAR,Types.INTEGER,
Types.INTEGER,Types.INTEGER,Types.INTEGER,Types.INTEGER,Types.TIMESTAMP,
Types.BIGINT,Types.INTEGER});
// Avoid concurrent modifications...
if(count==0){
int curentVersion=getJdbcTemplate().queryForObject(getQuery(CURRENT_VERSION_STEP_EXECUTION),
new Object[]{stepExecution.getId()},Integer.class);
throw new OptimisticLockingFailureException("Attempt to update step execution id="
+stepExecution.getId()+" with wrong version ("+stepExecution.getVersion()
+"), where current version is "+curentVersion);
}
stepExecution.incrementVersion();
}
}[BATCH_JOB_EXECUTION 테이블]
배치 잡의 실제 실행 기록. 잡이 실행될 때마다 새 레코드가 생성.
| 필드 | 설명 |
|---|---|
| JOB_EXECUTION_ID | 기본키 |
| VERSION | 낙관적인 Lock에 사용 |
| JOB_INSTANCE_ID | BATCH_JOB_INSTANCE 테이블 외래키 |
| CREATE_TIME | |
| START_TIME | |
| END_TIME | |
| STATUS | 잡 실행의 배치 상태. BatchStatus Enum. COMPLETED, STARTED 등 |
| EXIT_CODE | 실행의 종료 코드를 나타내는 문자열 |
| EXIT_MESSAGE | 작업이 종료된 방법에 대한 보다 자세한 설명을 나타내는 문자열입니다. 실패의 경우 여기에는 가능한 한 많은 스택 추적이 포함될 수 있습니다. |
| LAST_UPDATED |
[BATCH_JOB_EXECUTION_CONTEXT 테이블]
Job의 Execution Context 정보를 보관.
| 필드 | 설명 |
|---|---|
| JOB_EXECUTION_ID | 기본키 |
| SHORT_CONTEXT | A string version of the SERIALIZED_CONTEXT |
| SERIALIZED_CONTEXT | 직렬화된 Execution Context. Execution Context 직렬화는 Jackson2를 기본적으로 사용. |
[BATCH_JOB_EXECUTION_PARAMS 테이블]
매번 잡이 실행될 때마다 파라메터를 보관.
| 필드 | 설명 |
|---|---|
| JOB_EXECUTION_ID | 기본키 |
| TYPE_CODE | 파라니퍼 타입을 나타내는 문자열 |
| KEY_NAME | 파라미터 이름 |
| STRING_VAL | |
| DATE_VAL | |
| LONG_VAL | |
| DOUBLE_VAL | |
| IDENTIFYING | 파라미터가 식별자인지 나타내는 플래그 |
[BATCH_STEP_EXECUTION 테이블]
스텝이 실행될때 해당 스텝 Execution에 관한 정보를 저장.
| 필드 | 설명 |
|---|---|
| STEP_EXECUTION_ID | 기본키 |
| VERSION | 낙관적인 락에 사용 |
| STEP_NAME | 이름 |
| JOB_EXECUTION_ID | 외래키 |
| START_TIME | |
| END_TIME | |
| STATUS | 잡 실행의 배치 상태. BatchStatus Enum. COMPLETED, STARTED 등 |
| EXIT_CODE | 실행의 종료 코드를 나타내는 문자열 |
| EXIT_MESSAGE | 작업이 종료된 방법에 대한 보다 자세한 설명을 나타내는 문자열입니다. 실패의 경우 여기에는 가능한 한 많은 스택 추적이 포함될 수 있습니다. |
| LAST_UPDATED | |
| COMMIT_COUNT | |
| READ_COUNT | |
| FILTER_COUNT | |
| WRITE_COUNT | |
| READ_SKIP_COUNT | |
| PROCESS_SKIP_COUNT | |
| WRITE_SKIP_COUNT | |
| ROLLBACK_COUNT |
[BATCH_STEP_EXECUTION_CONTEXT 테이블]
Step Execution의 Context 정보를 저장.
| 필드 | 설명 |
|---|---|
| STEP_EXECUTION_ID | 기본키 |
| SHORT_CONTEXT | A string version of the SERIALIZED_CONTEXT |
| SERIALIZED_CONTEXT | 직렬화된 Execution Context. Execution Context 직렬화는 Jackson2를 기본적으로 사용. |
인메모리 JobRepository
외부 RDB를 사용하고 싶지 않을 때 사용. DefaultBatchConfigurer class에서 dataSource가 없으면 자동으로 설정해준다.
@EnableBatchProcessing
@SpringBootApplication(exclude = DataSourceAutoConfiguration.class)
public class InMemoryApplication extends DefaultBatchConfigurer{
@Override
public void setDataSource(DataSource dataSource) {
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(InMemoryApplication.class, args);
}
@Autowired
JobBuilderFactory jobBuilderFactory;
@Autowired
StepBuilderFactory stepBuilderFactory;
@Bean
public Job simpleJob() {
return jobBuilderFactory.get("job1")
.start(simpleStep1())
.incrementer(new RunIdIncrementer())
.build();
}
@Bean
public Step simpleStep1() {
return stepBuilderFactory.get("job1Step1")
.tasklet((contribution, chunkContext) -> {
return RepeatStatus.FINISHED;
})
.build();
}
}배치 인프라스트럭쳐 구성하기
BatchConfigurer Bean 구성 메카니즘
- 기본적으로 @EnableAutoConfiguration에 따라 BasicBatchConfigurer 사용
- BatchConfigurer 타입의 Bean이 존재하면 BasicBatchConfigurer 대신 사용
- DefaultBatchConfigurer는 커스텀하기 쉽게 배치 프로젝트에서 기본적으로 제공
@EnableBatchProcessing
- @Import(BatchConfigurationSelector.class)
- @EnableBatchProcessing의 modular가 디폴트로 false
- BatchConfigurationSelector.class > selectImports() 에서 new String[] { SimpleBatchConfiguration.class.getName() }; 리턴
- SimpleBatchConfiguration.class에서 여러 핵심 Bean(JobRepository/ JobLauncher 등) 의 프록시 생성
- 프록시에 의한 실행 순서
- 타겟소스는 ReferenceTargetSource extends AbstractLazyCreationTargetSource implements TargetSource
- 실제 구동 중 해당 오브젝트 사용 시
- advice인 PassthruAdvice에서 invoke시 TargetSource의 getTarget() 실행
- AbstractLazyCreationTargetSource에 getTarget() 구현체가 있고 이때 ReferenceTargetSource에 구현된 createObject() 실행.
- createObject() 에서 initialize() 실행하고 AtomicReference가 감싸고 있던 실제 오브젝트 반환
- initialize()에서 BatchConfigurer 구현체 찾아서 각 인프라 오브젝트 세팅. 이때 커스터마이징된 오브젝트 설정
- 참고로 SimpleBatchConfiguration.class의 상위 클래스인 AbstractBatchConfiguration에서 StepScope와 JobScope 생성
- 프록시에 의한 실행 순서
private <T> T createLazyProxy(AtomicReference<T> reference, Class<T> type) {
ProxyFactory factory = new ProxyFactory();
factory.setTargetSource(new ReferenceTargetSource<>(reference));
factory.addAdvice(new PassthruAdvice());
factory.setInterfaces(new Class<?>[] { type });
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
T proxy = (T) factory.getProxy();
return proxy;
}BatchConfigurer 인터페이스
public interface BatchConfigurer {
JobRepository getJobRepository() throws Exception;
PlatformTransactionManager getTransactionManager() throws Exception;
JobLauncher getJobLauncher() throws Exception;
JobExplorer getJobExplorer() throws Exception;
}
DefaultBatchConfigurer class가 BatchConfigurer를 기본적으로 구현했기 때문에 인프라를 커스텀하게 구성하고 싶다면 DefaultBatchConfigurer를 상속받아 필요한 메소드만
오버라이드하면 된다.
JobRepository 커스터마이징하기
@Configuration
public class CustomBatchConfigurer extends DefaultBatchConfigurer {
@Autowired
@Quilfier("someDatasource")
DataSource ds;
@Override
protected JobRepository createJobRepository() throws Exception {
JobRepositoryFactoryBean factory = new JobRepositoryFactoryBean();
factory.setDataSource(ds);
factory.setTransactionManager(getTransactionManager());
factory.setIsolationLevelForCreate("ISOLATION_REPEATABLE_READ");
factory.afterPropertiesSet();
return factory.getObject();
}
}JobRepositoryFactoryBean을 통하여 JobRepository을 생성한다.
JobRepositoryFactoryBean은 JobRepository 생성하기 위한 여러가지 기능을 제공한다.
(자세한 내용은 책 190p 참고)
createJobRepository()는 DefaultBatchConfigurer에 있는 @PostConstruct public void initialize()에 의해서 실행된다.
afterPropertiesSet()을 호출하고 factory.getObject()을 리턴한다. 위 두개 메서드를 컨테이너에서 따로 호출하지 않기 때문에 create.. 류를 호출할때는 수동으로 호출하는 것을 유의해야한다. 커스터마이징 않을때는 DefaultBatchConfigurer가 알아서 호출해준다.
해당 프로젝트에 두 개 이상의 데이터소스가 존재한다면 명시적으로 선택 할 수 있다.
TransactionManager 커스터마이징하기
DefaultBatchConfigurer 에서는 트랜잭션 매니저를 setDatasource에서 생성한다(DataSourceTransactionManager)
따라서 protected create... 류를 오바라이딩 하지 않고 BatchConfigurer 인터페이스의 getTransactionManager()를 오버라이딩한다.
@Configuration
public class CustomBatchConfigurer extends DefaultBatchConfigurer {
@Autowired
PlatformTransactionManager transactionManager;
@Override
public PlatformTransactionManager getTransactionManager() {
return this.transactionManager;
}
}
JobExplorer 커스터마이징하기
JobExplorer는 JobRepository에서 제공하는 API에 접근하여 읽기 전용으로 제공.
@Configuration
public class CustomBatchConfigurer extends DefaultBatchConfigurer {
@Autowired
DataSource ds;
@Override
protected JobExplorer createJobExplorer() throws Exception {
JobExplorerFactoryBean jobExplorerFactoryBean = new JobExplorerFactoryBean();
jobExplorerFactoryBean.setDataSource(this.ds);
jobExplorerFactoryBean.afterPropertiesSet();
return jobExplorerFactoryBean.getObject();
}
}JobLauncher 커스터마이징하기
JobLauncher는 스프링 배치 잡을 실행하는 진입점. 기본으로 SimpleJobLauncher 사용. 하지만 커스텀 할 필요가 생길 경우 아래와 같은 방식으로 커스터마이징 가능.
@Configuration
public class CustomBatchConfigurer extends DefaultBatchConfigurer {
@Autowired
DataSource ds;
@Override
protected JobRepository createJobRepository() throws Exception {
JobRepositoryFactoryBean factory = new JobRepositoryFactoryBean();
factory.setDataSource(ds);
factory.setTransactionManager(getTransactionManager());
factory.setIsolationLevelForCreate("ISOLATION_REPEATABLE_READ");
factory.afterPropertiesSet();
return factory.getObject();
}
@Override
protected JobLauncher createJobLauncher() throws Exception {
SimpleJobLauncher jobLauncher = new SimpleJobLauncher();
jobLauncher.setJobRepository(this.createJobRepository());
jobLauncher.afterPropertiesSet();
return jobLauncher;
}
}데이터베이스 구성하기
spring:
datasource:
driverClassName:com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
url:jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/spring_batch
username:root
password:mysql
batch:
initialize-schema:always
batch.initialize-schema : 스프링 배치 실행 시 스크립트 실행여부 설정
- 속성값
- always : 항상 스크리브 실행. 개발시에 적합.
- never : 스크립트 실행 안함
- embedded : 내장 데이터베이스 사용 시. 실행할때마다 초기화 된다는 가정으로 사용.
잡 메타데이터 사용하기
JobExplorer
배치 정보 데이터베이스에서 정보를 읽어 오기 위한 용도. 읽기 전용 뷰를 제공.
JobRepository 인터페이스와 같이 데이터베이스에 직접 접근.
public interface JobExplorer {
/**
* Fetch {@link JobInstance} values in descending order of creation (and
* therefore usually of first execution).
*
* @param jobName the name of the job to query
* @param start the start index of the instances to return
* @param count the maximum number of instances to return
* @return the {@link JobInstance} values up to a maximum of count values
*/
List<JobInstance> getJobInstances(String jobName, int start, int count);
/**
* Retrieve a {@link JobExecution} by its id. The complete object graph for
* this execution should be returned (unless otherwise indicated) including
* the parent {@link JobInstance} and associated {@link ExecutionContext}
* and {@link StepExecution} instances (also including their execution
* contexts).
*
* @param executionId the job execution id
* @return the {@link JobExecution} with this id, or null if not found
*/
@Nullable
JobExecution getJobExecution(@Nullable Long executionId);
/**
* Retrieve a {@link StepExecution} by its id and parent
* {@link JobExecution} id. The execution context for the step should be
* available in the result, and the parent job execution should have its
* primitive properties, but may not contain the job instance information.
*
* @param jobExecutionId the parent job execution id
* @param stepExecutionId the step execution id
* @return the {@link StepExecution} with this id, or null if not found
*
* @see #getJobExecution(Long)
*/
@Nullable
StepExecution getStepExecution(@Nullable Long jobExecutionId, @Nullable Long stepExecutionId);
/**
* @param instanceId {@link Long} id for the jobInstance to obtain.
* @return the {@link JobInstance} with this id, or null
*/
@Nullable
JobInstance getJobInstance(@Nullable Long instanceId);
/**
* Retrieve job executions by their job instance. The corresponding step
* executions may not be fully hydrated (e.g. their execution context may be
* missing), depending on the implementation. Use
* {@link #getStepExecution(Long, Long)} to hydrate them in that case.
*
* @param jobInstance the {@link JobInstance} to query
* @return the set of all executions for the specified {@link JobInstance}
*/
List<JobExecution> getJobExecutions(JobInstance jobInstance);
/**
* Retrieve running job executions. The corresponding step executions may
* not be fully hydrated (e.g. their execution context may be missing),
* depending on the implementation. Use
* {@link #getStepExecution(Long, Long)} to hydrate them in that case.
*
* @param jobName the name of the job
* @return the set of running executions for jobs with the specified name
*/
Set<JobExecution> findRunningJobExecutions(@Nullable String jobName);
/**
* Query the repository for all unique {@link JobInstance} names (sorted
* alphabetically).
*
* @return the set of job names that have been executed
*/
List<String> getJobNames();
/**
* Fetch {@link JobInstance} values in descending order of creation (and
* there for usually of first execution) with a 'like'/wildcard criteria.
*
* @param jobName the name of the job to query for.
* @param start the start index of the instances to return.
* @param count the maximum number of instances to return.
* @return a list of {@link JobInstance} for the job name requested.
*/
List<JobInstance> findJobInstancesByJobName(String jobName, int start, int count);
/**
* Query the repository for the number of unique {@link JobInstance}s
* associated with the supplied job name.
*
* @param jobName the name of the job to query for
* @return the number of {@link JobInstance}s that exist within the
* associated job repository
*
* @throws NoSuchJobException thrown when there is no {@link JobInstance}
* for the jobName specified.
*/
int getJobInstanceCount(@Nullable String jobName) throws NoSuchJobException;
}public class ExploringTasklet implements Tasklet {
private JobExplorer explorer;
public ExploringTasklet(JobExplorer explorer) {
this.explorer = explorer;
}
public RepeatStatus execute(StepContribution stepContribution,
ChunkContext chunkContext) {
String jobName = chunkContext.getStepContext().getJobName();
List<JobInstance> instances =
explorer.getJobInstances(jobName,
0,
Integer.MAX_VALUE);
System.out.println(
String.format("There are %d job instances for the job %s",
instances.size(),
jobName));
System.out.println("They have had the following results");
System.out.println("************************************");
for (JobInstance instance : instances) {
List<JobExecution> jobExecutions =
this.explorer.getJobExecutions(instance);
System.out.println(
String.format("Instance %d had %d executions",
instance.getInstanceId(),
jobExecutions.size()));
for (JobExecution jobExecution : jobExecutions) {
System.out.println(
String.format("\tExecution %d resulted in Exit Status %s",
jobExecution.getId(),
jobExecution.getExitStatus()));
}
}
return RepeatStatus.FINISHED;
}
}'스프링 배치 완벽 가이드 2판' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 9장 ItemWriter -2 (0) | 2022.03.31 |
|---|---|
| 7장 ItemReader - 1부 (~json) (0) | 2022.03.31 |